706 XII. SYNOPSIS OP TRADE AND INDUSTRIAL LEGISLATION.
T able 143. Patent Applications filed in Sweden during 1885—1913.
Refrigerating devices .
Baking industry . . .
Clothing industry
Illum in a tio n ................
Bleaching, dying, calendering
(of textile pro-
j ducts) . . • • ■
Blowing machines and
v entilators................
I Bookbinding and books
Brush and paintbrush
manufacture • • • •
F u e l • ■
Fireplace devices • • •
Electrotechnics . . . ,
Explosives and match
industry . . • . • # ■ •
Fats and mineral oils .
Plaiting and knitting .
Photography . . .
Colours and dyes, varnishes
and other paints
Articles of Food . . .
Tanning and currying .
Cas m a k in g ................
Casting and moulding
■ (of metals) . . .
G-lass industry . . . .
Mining and mining
structures ». . . • .
Manures........................
Travelling utensils . .
Hat manufacture . . .
i Hygienics and sick nursing
. . . • • • ’ i' •
Building industries . .
instruments and measuring
apparatus • • •
Iron and steel manufacture
....................
Railways and Tramway# I
Chemical apparatus and
processes . . • •
Controlling and regist-
rir% devices . . -"\f .
Haberdashery . . • •
Milling industry . . .
Agriculture, forestry, and
• g a rd e n in g .................. I
Clay, brick and tile, j
cement and stone in- j
d u s tr ie s ....................
Lifting devices . . . .
Locks, bolts, fittings .
Ore concentration and j
re fin in g ....................
Machine Parts . . . .
Sundry materials . . .
Metal work, chemical . I
101 115 216 Metal work, mechanical
184 102 286 Metal wire and metal-
182 230 412 sheet manufacture - .
495 719 1214 Metallurgy and smelting
Motors ............................
Musical instruments . .
281 378 659 Furniture and domestic
u te n s ils ....................
41 136 177 Pa-per articles and paper
156 98 254 w o r k ........................
Paper and wood pulp
80 75 155 manufacture . . . .
331 268 599 P r e s s e s ........................
291 562 853 Pumps . . . ._. • • •
1067 2 735 3802 Regulators for power
e n g in e s ....................
151 427 578 Rope making . . .
112 229 341 Life saving and salvage
52 81 133 Saddlery, carriages, bi69
197 266 cycles ........................
Salesmanship................
126 202 328 Harness and carriage
339 580 919 ’ gear ............................
43 131 174 S ig n a llin g ....................
215 453 668 Ship-huilding and navigation
. . . . . . .
95 196 291 Firearms, armour, am59
• 205 264 munition . . _. .
Boot and shoe manu87
115 202 facture . . . . . . .
90 93 183 Writing and drawing
149 ,1 1 6 265 materials. . . . • •
45 32 77 Cutting to o ls................
Slaughtering and meat
292 446 738 cu rin g ................... •
476 478 954 Grinding and polishing
Sugar industry . . - .
616 704 1320 Spinning and carding .
Sports and athletics .
£04 293 497 Spinning fibres and their
465 951 1416 tr e a tm e n t ................
Sewing machines .
362 1240 1602 Devices for tapping or
bottling and retailing
187 265 452 liquids .. . . . . - ■
288 232 520 Tobacco industry . . .
182 239 421 Drying apparatus . . .
T ra n s p o rt....................
2 849 1083 3 932 Printing and stamping
Wood working and refining,
........................
334 670 1004 Heating devices . . . ’ .
179 i 137 316 Watch making . . . .
641 304 945 Water works . . . . .
Water closets and drai165
204 369 nage . . . . . .
1222 1036 '2258 Water and wind motors
73 299 372 T o o l s ............................
29 133 162 Textile industry . . .
661 1 112 1773
15 ' '58 73
379 ' 717 1096
694 709 1403
212 131 343
892 795 2 687
121 234 355
242 650 892
30 ■ -69 99
199 197 396!
56 631 119!
.‘11 25 36
167 183 350
825 1046 1871
232 255 487
201 78j 279
177 223 400
404 616 1020
394 1191 1585
233 565 798
262 142 404
106 68- 174
45 56 101
93 98 191
60 ■ 233 293
45 141 186!
355 284 639;
18 77 95
64 ■ 181 245
406 537 943
25 166 191
228 193 421
■412 3601 772
187 632 819
#62 603 1465
828 527 1355
80 80 160
40 88 128
139 140 279
160 ■138 298
204 168 372
82 1 2181 300
Classes of industry Classes of industry
The inventor
domiciled
Sweden
T a b l e 143 (cont.) Patent Applications filed in Sweden during 1885—1913.
Classes of industry
The inventor
domiciled
Total Classes of industry
The inventor
domiciled
Total
in
Sweden abroad in
Sweden abroad
1 Construction of Roads 198 181 379 Brewing and distilling 87 255 342
Steam engines . . . . 331 512 843
| Steam boilers . . . . 228 482 710 Total 26 095 32 666 58 761
concession, with such restrictions and conditions and against such compensation
as it deems to be fair and reasonable.
Thus, under this enactment, which was embodied in the Act of May 9, 1902,
the patentee does not actually lose his patent by neglecting to work it, as was
formerly the case in- Sweden, and is still so in most other countries, but merely
exposes himself to the risk of a compulsory license (tvângslicens) being ordered
by the Court.
Legislation in Sweden has thus solved, and, as experience seems to show,
happily solved the difficult question how, without prejudice to the interests of
home industries, to enforce obligation of working a patent in such a manner
that the obligation shall not be unnecessarily onerous to the patentee to fulfil,
nor yet shall render the validity of the patent precarious.
When an action for a compulsory license is brought before the City Court
of Stockholm, three experts : on industrial questions besides the qualified number
of judges shall sit and have a vote in the Court, these experts annually being
nominated by the patent authorities. "
We. see here the germ of a special court for actions relating to industrial
rights of property.
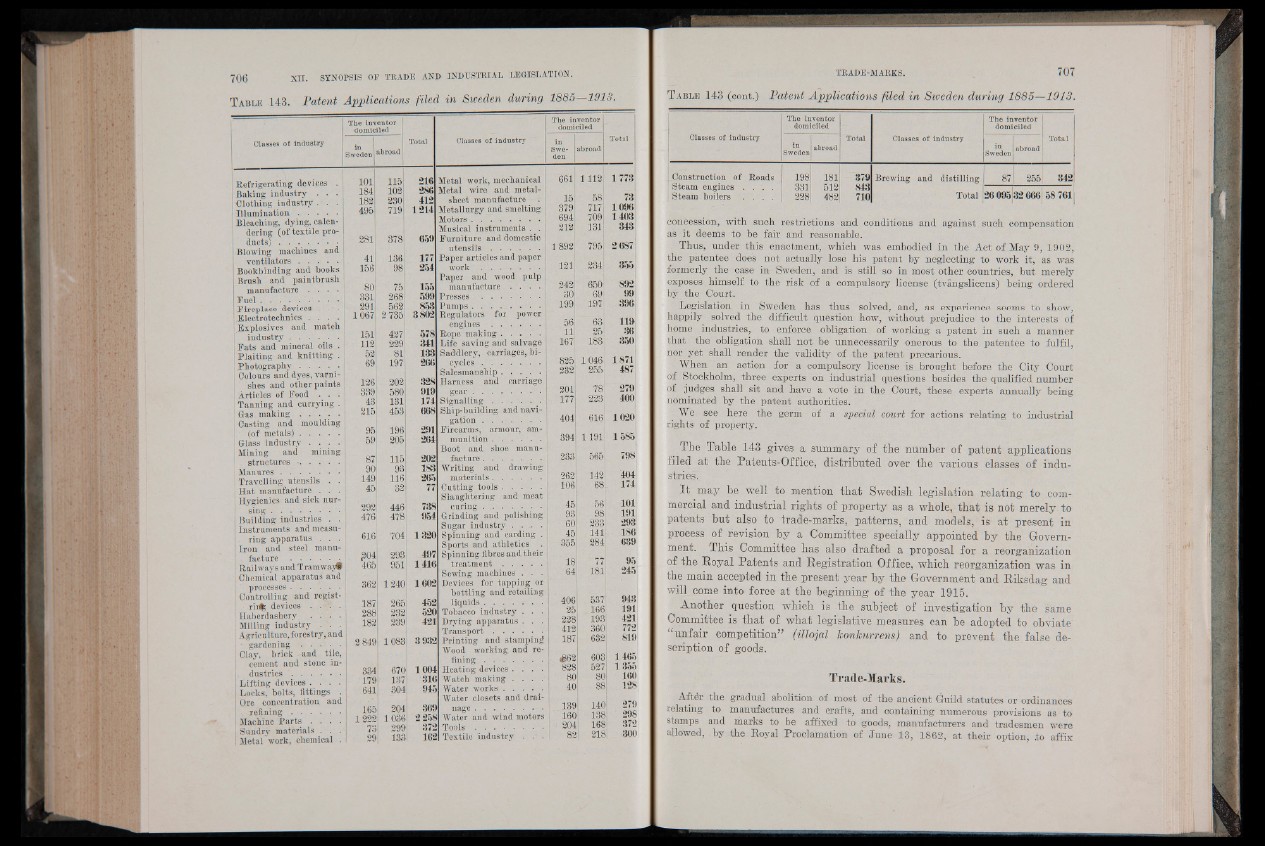
The Table 143 gives a summary of the number of patent applications
filed at the Patents-Office, distributed over the various classes of indu-
striesT
It may be well to mention that Swedish legislation relating to commercial
and industrial rights of property as a whole, that is not merely to
patents but also to trade-marks, patterns, and models, is at present in
process of revision by a Committee specially appointed by the Government.
This Committee has also drafted a proposal for a reorganization
of the Royal Patents and Registration Office, which reorganization was in
the main accepted in the present year by the Government and Riksdag and
will come into force at the beginning of the year 1915.
Another question which is the subject of investigation by the same
Committee is that of what legislative measures can be adopted to obviate
“unfair competition” (illojal konkurrens) and to prevent the false description
of goods.
Trade-Marks.
Aftêr the gradual abolition of most of the ancient Guild statutes or ordinances
relating to manufactures and crafts, and containing numerous provisions as to
stamps and marks to be affixed to goods, manufacturers and tradesmen were
allowed, .by the Royal Proclamation of June 13, 1862, at their option, .to affix