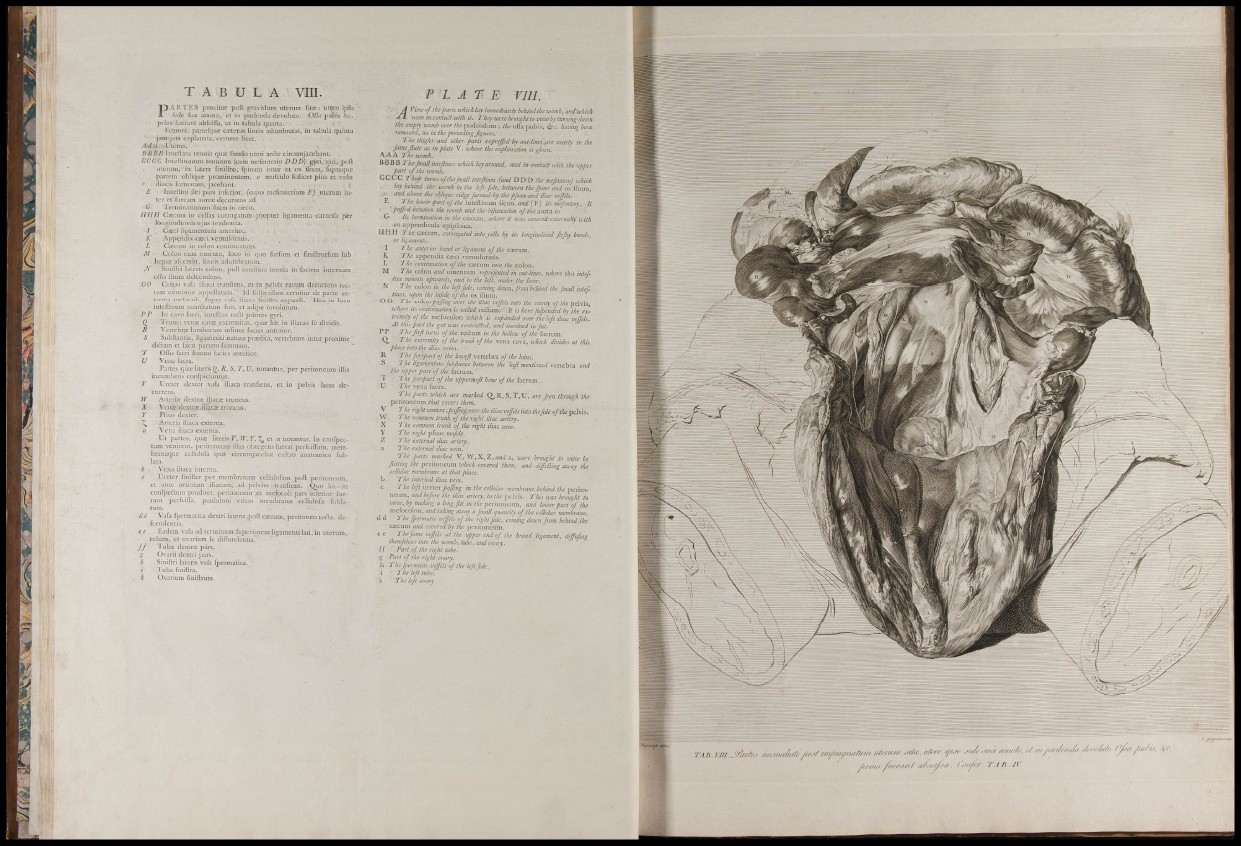
T A B U L A V I I I .
PA R T E S proximc poft gravidum utcrum filac ; utero ipfo
ll-rlc fua anioLo, ct in pudenda devoluto. OíTa pubis &c.
j)iius iucrant ablciiTa, ut in tabula quarta.
Femora, pandquc canteras lineis adúmbralas, in tabula quinta
jam jam cxplanata, cernere licet.
J ^ IA Uterus.
B BBB Inteilina tenuia quae fundo uteri artìe circumjacebant.
CCCC Inteílinorum Leimium (cum mefenterio DDD) gyri,-qui, poil
ilium," iiipraque
mufculo fcilicet pfoa ec vails
ulerum, in latere fmiftro, fpiri
partem oblique prominentem,
iliacis formatam, jacebant.
E In teilin i ilei pars inferior, (cujus mefenterium F) uterum inter
et íurcam aorta: decurrens ad
G 'i erminationem fuam in casco.
II II II Ciccum in celias corrugatum propter ligamenta carnofa per
longiiudin'em ejus tendentia.
/ Cscci ligamentum anterius.
IC Appendix oEci vemifdnnis.
L Cxcum in colon continiiatum.
M Colon cum omento, loco in quo furfum et finiftrorfum fub
liepar afcendit, lineis adumbratum.
X Siniñrl lateris colon, poft inteilina tenuia in facicm internam
offis ilium defcendens.
0 0 Colon vafa iliaca tranfiens, et in pelvis ca\aim decurrens rectum
continuo appellaiuni. Id fufpenfum cernitur de parte extrema
mcfocoli, fupra vafa iliaca finiflra expanfi. Hoc in loco
inteílinum coardatum fuit, et adipe involutum.
P P In cavo facri, inteiUni redi priores g)TÌ.
(¿ Trunci xcnx cavsc extremitas, quas liic in iliacas fe dividit.
R Vertebra: lumborum infima: facies anterior.
5 Subílantia, ligamenti natura pi-asdita, vertebrara inter proximc
ditìam et facri partem fummam.
T OfTis facri fummi facies anterior.
U Vena facra.
Partes qrnc lÍLerisí¿, R, S, T", £/, notantur, per peritoneum illis
incumbens confpiciuntur.
V Ureter dexter vafa iliaca tranfiens, et in pelvis latus de-
//
Arterias dextne iliacíE truncus.
Venx dextne iliacx truncus.
Pfoas dexter.
Arteria iliaca externa.
Vena iliaca externa.
Ut partes, qua Uteris V, IV, T, X¿ et a notantur, in confpectum
venircnt, peritoneum illas obtegens fuerat perfciffum, raembranaque
cellulofa qua: circumjaccbat cultro anatomico fublata.
"N^'ena iliaca interna.
Ureter üniíler per membranam cellulofam poíl peritoneum,
et ante arteriam iliacam, ad pehim tranfiens. Quo hie. in
confpedum prodiret, peritoneum et mefocoli pars inferior fuerant
pcrfciiTa, pauluknn etiam membranas cellulofa: fublatum.
Vafa fpermatica dextri lateris poil caecum, peritoneo teña, defcendentia.
Eadem \-afa ad terminum fuperiorcm ligamenti Iati, in uterum,
tubam, et ovarium fe diifundentia.
Tubae dextne pars^
0\'arii dextri pars.
Siniilri lateris vafa fpermatica.
Tuba fmiilra.
Ovarium finiilrum.
P L A T E VI I I . ^
. • A Viemof thepartswhichlay immediately behindthewomb.aniwhich
•ii were in contall with it. They were brought lo view by turning down
the empty womb over the pudendum ; the ofla pubis, ¿re. having been
removed^ as in the preceding figures.
The thighs and other parts exprejei by out-lines,arc nearly in the
Jameßate as in plate V. where the explanation is given.
A A A The womb. . . . ,
BBBB Thejmallinteßincs which lay around, and in contaH with the upper
part of the womb.
CCCC Thoje turns ofthejmall inteßines fand DDTl the mejentery) which
lay behind the womb in the left fide, between the Jpine and os ilium,
• and above the oblique ridge firmed by the pJoa-!> ami iliac vejeb.
E The lower part of the hAdiXimimiXcou,and [\'] its mefintery. It
' pajfed between the womb and the bifurcation of the aorta to
G Its termination in the ca;cum, where it was covered externally with
an appeudicula epiploica.
H H H The CECum, corrugated into cells by its longitudinalßeßiy bands,'
or ligaments.
I The anterior band or ligament of the CKCum.
K The appendix cccci \-ermiformis.
L The continuation of the ciccum into the colon.
M The colon and omentum reprefented in out4ines, where this intcf
tine mounts upwards, and to the left, under the liver.
N The colon in the left fide, coming down, from behind the fmall inteftines,
upon the infide ¿f the os ilium.
0 O The colon pajing over the iliac veßls into the cavity of the pelvis,
where its continuation is called reflum. It is here fujpended by the extremity
of the mcfocolon which is expanded over the left iliac vefjels.
At this part the gut was contrasted, and involved in fat.
P P Thefirß turns of the rcclum in the hollow of the facrum.
Q, The extremity of the trunh of the vena cava, which divides at this
place into the iliac veins.
R The forepart of the loweßvenAa of the loins.
S The ligamentous fubßance between the laß mentioned vertebra and
the upper part of the facrum.
T The forepart of the uppermoß bone of the facrum.
U The \ ena facra.
The parts which are marked q,R,S,T,U, are feen through the
peritoneum that covers them.
V The right UTiititT,paßngover the iliac vejels into the fide o / i i i pelvis.
W The common trunk of the right iliac artery.
X The common trunk of the right iliac vein.
Y The right pfoas mufck.
2 The external iliac artery.
a The external iliac vein.
The parts marked V, W, X, Z, and a, were brought to vim by
fitting the peritoneum which covered them, and dißäing away the
cellular membrane at that place.
b The internal iliac vein.
c The left ureter paßng in the cellular membrane behind the peritoneum,
and before the iliac artery, to the pelvis. This was brought to
view, by making a longßit in the pcritoneiuri, and lower part of the
mefocolon, and taking away a fmall quantity of the cellular membrane.
d d Thefpermatic veßels of the right fide, coming down from behind the
caecum and covered by the peritoneum,
e e The fame veßels at the upper end of the broad ligament, diffufing
themfelves into the womb, tube, and ovary.
f f Part of the right tube,
g Part of the right ovary.
h Thefpermatic veßels of the left fide.
1 The left lube.
k The left ovary.
'/://(. //nI/I,•,//,//!'/if.in'/ii/iM-i/fii!à///i I//I'I7IIII .Ii/ir. ii/i-ri' ///-H' -K-i/r .'i/'i ,iiii<'^".
/ii-iii.i /i/.mi/i' . ^ T. / / ; . / / :
- / / ^'/.Irl /lllkt,