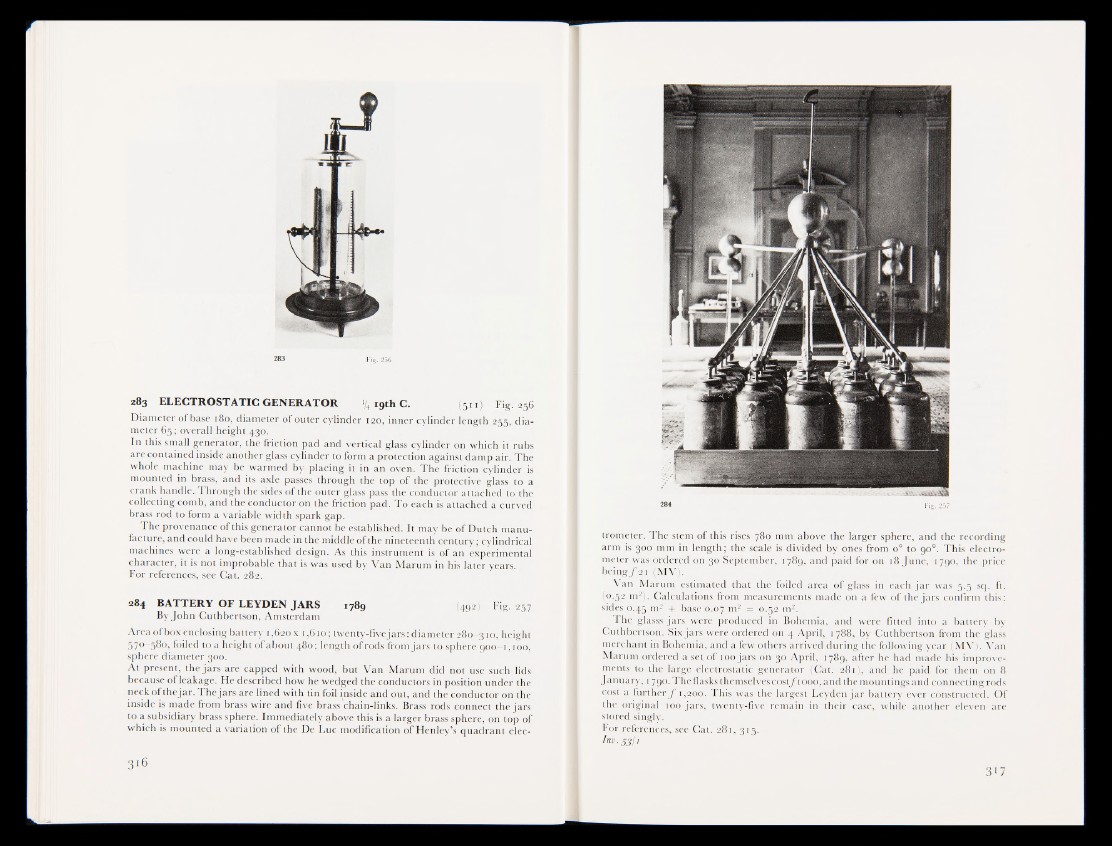
283 256
283 ELECTROSTATIC GENERATOR ^ i9th C. I5 1 1 J Fig. 256
Diameter ofbase 180, diameter of outer cylinder iao, inner cylinder length R § , diameter
65; overall height 430.
In this small generator, the friction pad and vertical glass cylinder on which it ruhs
are contained inside another glass cylinder to form a protection against damp air. The
whole machine may be warmed by* placing it in an oven. The friction cylinder is
mounted in brass, and its axle passes through the top of the protective glass to a
crank handle. Through the sides of the outer glass pass the conductor attached tfethe
collecting comb, and the conductor on the friction pad. To each is attached a curved
brass rod to form a variable width spark gap.
The provenance of this generator cannot be established. It may be of Dutch manufacture,
and could have been made in the middle of the nineteenth century; cylindrical
machines were a long-established design. As this instrument is of an experimental
character, it is not improbable that is was used by Van Marum in his later years.
For references, see Cat. 282.
284 BATTERY OF LEYDEN JARS 1789 (49s| Fig. 25I
By John Cuthbertson, Amsterdam
Area ofbox enclosing battery i ,6 2 0 x 1 ,6 1 0 ; twenty-five jars: diameter 2 8 0 - 3 1 0 , height
570—5®° > foiled to a height of about 4 8 0 ; length of rods from jars to sphere 9 0 0—1 ,1 0 0 ,
sphere diameter 300.
At present, the jars are capped with wood, but Van Marum did not use such lids
because of leakage. He described how he wedged the conductors in position under the
neck ofthejar. The jars are lined with tin foil inside and out, and the conductor on the
inside is made from brass wire and five brass chain-links. Brass rods connect the jars
to a subsidiary brass sphere. Immediately above this is a larger brass sphere, on top of
which is mounted a variation of the De Luc modification of Henley’s quadrant electrometer.
The stem of this rises 780 mm above the larger sphere, and the recording
arm is 300 mm in length; the scale is divided by ones from 0° to 90°. This electrometer
was ordered on jgio September, 1789, and paid for on 18 June, 1790, the price
being ƒ 21 (MVj, ...
Van Marum estimated that thé foiled area of glass in'each jar was 5.5 sq. ft.
(.0.52 in2). Calculations from measurements made on a few of the jars confirm this:
sides 0.45 m^fflbase 0.07 m2^Ho.§S m2.
The glasss jars were produced in Bohemia, and were fitted into a battery by
Cuthbertson. Six jars were ordered on 4 April, 1788, by Cuthbertson from the glass
merchant in Bohemia, and a few others arrived during the following year (MV). Van
Marum ordered a set of 100 jars on 30 April, 1789, after he had made his. improvements
to the large electrostatic generator (Cat. 281), and he paid for them on 8
January, 1790. The flasks themselves cost/i 000, and the mountings and connecting rods
cost a further ƒ 1,200. This was the largest Leyden jar battery ever constructed. Of
the original 100 jars, twenty-five remain in their case, while another eleven are
stored singly.
For references, see Cat. 281, 315.* •
Inv. ■