m
• y
v!
i i '
m
E X P L A N A T I O N OF THE TABLES. 143
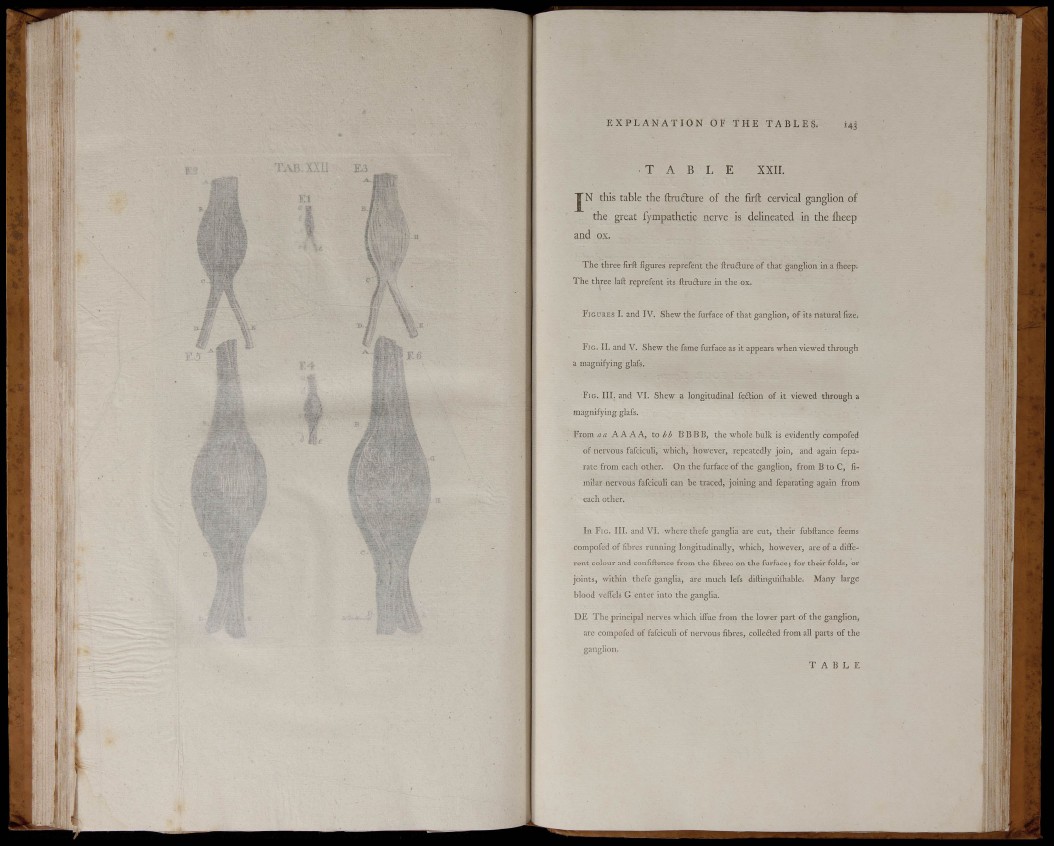
T A B L E XX r i .
J N this table the ftruéture of the firfl: cervical ganglion of
the great fympathetic nerve is delineated in the flieep
and ox.
The three flrfl: figures reprefent the ftrudture of that gangUon in a iheep;
The three laft reprefent its llructure in the ox.
FIGURES L and IV. Shew the furface of that ganglion, of its natural iize.
FJG. II. and V. Shew the fame furface as it appears when viewed through
a magnifying glafs.
FIG. III. and VI. Shew a longitudinal feétion of it viewed through a
magnifying glafs.
From ûa AAAA, to BBBB, the whole bulk is evidently compofed
of nervous fafciculi, which, however, repeatedly join, and again feparate
from each other. On the furface of the ganglion, from B to C, fimilar
nervous fafciculi can be traced, joining and feparating again from
each other.
In FIG. III. and VI. where thefe ganglia are cut, their fubilance feems
compofed of fibres running longitudinally, which, however, are of a different
colour and confiftence f rom the fibres on the furface; for their folds, or
joints, within thefe ganglia, are much lefs diilinguiihable. Many large
blood veflcls G enter into the ganglia.
DE The principal nerves which ilTue from the lower part of the ganglion,
are compofed of fafcicuU of nervous fibres, colleited from all parts of the
ganglion.
T A B L E
HJ' îiiiti
m